Selection of the right to a seal is very important to the success of the use of the pump. To get the best pump reliability, insulation must be appropriate choice between the environment and the type of seal used.
Fundamentals of Insulation (Seal)
There are two types of seals: static and dynamic.
Static seals are used where there is no movement going meetings between the two surfaces to be sealed. Gaskets and O-rings are a common example of a static seal.
Dynamic seals are used where there are surfaces that move relative to each other. Dynamic seals for example are used on a rotating shaft and delivers power through a wall of the tank (Figure 1), through the casing of the pump (Figure 2), or through the other rotating equipment such as filters or screens.
In centrifugal pumps, the fluid entering into pump through the 'suction' at the center (eye) of the impeller is rotating. (Figures 3 and 4).
At the time of the fan impeller rotates, they deliver the movement to include a product, which then leaves the impeller, collected in the pump housing (casing) and leaves the pump through pressure on the exit side (discharge) pump.
Discharge pressure will suppress some products down behind the impeller to the shaft, where he will try out all the rotating shaft. Pump manufacturers use a variety of techniques to reduce the pressure of the product to try out. Some common ways are:
The addition of a counterweight hole (hole balance) through the impeller to provide a way for the pressure that will come out through the suction side of the impeller.
The addition of the fan on the back side of the impeller (back pump-out vanes).
However, as long as there is no way to reduce this pressure completely, sealing equipment is absolutely necessary to restrict the release of the product. As baffle compression (packing) or mechanical sealing (mechanical seals).
Stuffing Box Packing
Setting the use of 'stuffing box' is shown in the figure below. It consists of:
5 ring packing.
A lantern ring is used to inject peluamas and or to dispose of liquid
A suppressor (gland) to hold the packing and keep the pressure needs tightening packing adapted to the conditions.
Discharge pressure will suppress some products down behind the impeller to the shaft, where he will try out all the rotating shaft. Pump manufacturers use a variety of techniques to reduce the pressure of the product to try out. Some common ways are:
The addition of a counterweight hole (hole balance) through the impeller to provide a way for the pressure that will come out through the suction side of the impeller.
The addition of the fan on the back side of the impeller (back pump-out vanes).
However, as long as there is no way to reduce this pressure completely, sealing equipment is absolutely necessary to restrict the release of the product. As baffle compression (packing) or mechanical sealing (mechanical seals).
Stuffing Box Packing
Setting the use of 'stuffing box' is shown in the figure below. It consists of:
5 ring packing.
A lantern ring is used to inject peluamas and or to dispose of liquid
A suppressor (gland) to hold the packing and keep the pressure needs tightening packing adapted to the conditions.
Method of lubrication on the packing depends on liquid pumped ko0ndisi and also pressure on the stuffing box. When the stuffing box pressure above atmospheric pressure and the fluid is clean and not corrosive pressed, the fluid in the pump that is functioning as a gasket lubricant. (Figure 6).
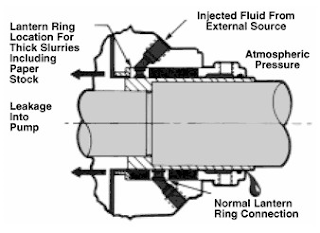
When the pressure in the stuffing box under atmospheric pressure, a lantern ring in pairs and lubricant injected into the stuffing box. (figure 7). A bypass pipe from the pump to the side of the press liaison lantern ring is generally used to provide a flow of liquid when the liquid is clean.
When the liquid being pumped is dirty or air particles, need to clean lubricating fluid injected from the outside through the lantern ring (figure 8). The flow of as much as 0.2 to 0.5 gpm faucet required and a regulator and flowmeter needs to be installed to get accurate flow. Lantern rings are usually mounted in the middle of the stuffing box, but for highly viscous liquids such as raw materials recommended paper is installed in the neck to avoid blockage of the stuffing box lantern ring.
Packing house (glands) in Figure 5 to 8 is a type of 'quench gland'. Water, oil or other fluids can be injected into the gland to reduce heat shaft, it can minimize the heat transfer from the shaft to the bearing. Allow for this reason that the working temperature of the pump is higher than the design of temperature bearing and pelumas.Tipe 'quench gland' the same can be used to prevent the release of toxic or hazardous fluids out into the outside air around the pump. It is called 'smothering gland', by draining fluid from the outside and bring unwanted leakage into the trench or former liquid collection tank.







A functional well is vital for a consistent and clean water supply. Over time, wells can encounter issues such as low water pressure, contamination, or mechanical failures. Professional well repair near me services address these problems promptly, ensuring your water system operates efficiently. Experts diagnose issues, clean wells, repair pumps, and restore water flow.
ReplyDelete